*WAEC GCE GOVERNMENT OBJ*
*Pls Kindly Trace It From Your System. The options are being reshuffled u might see number one as any number so trace and be fast and open ur eye open like a criminal and trace well good luck*
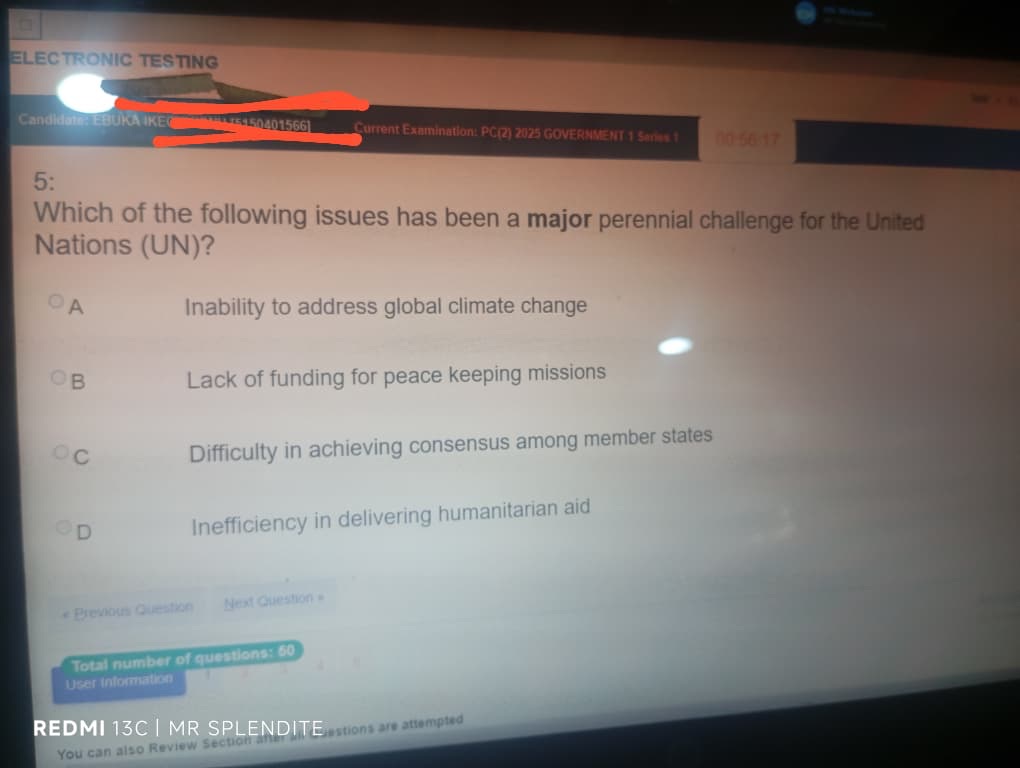
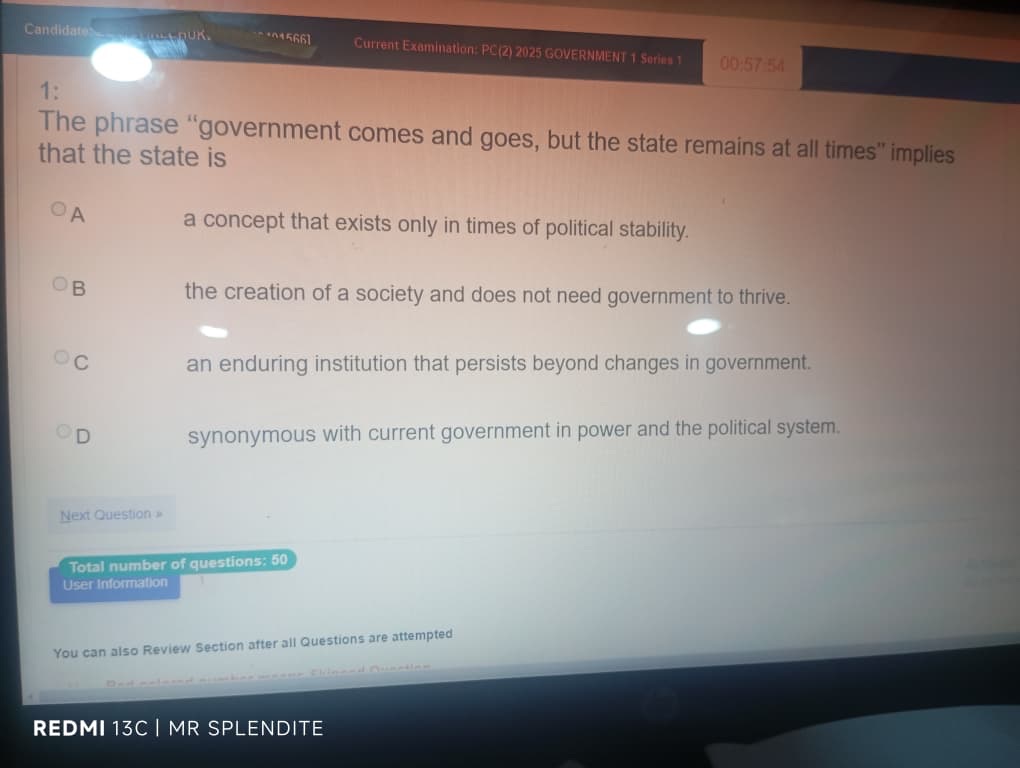
1; (C) an enduring institution that persists beyond changes in government.
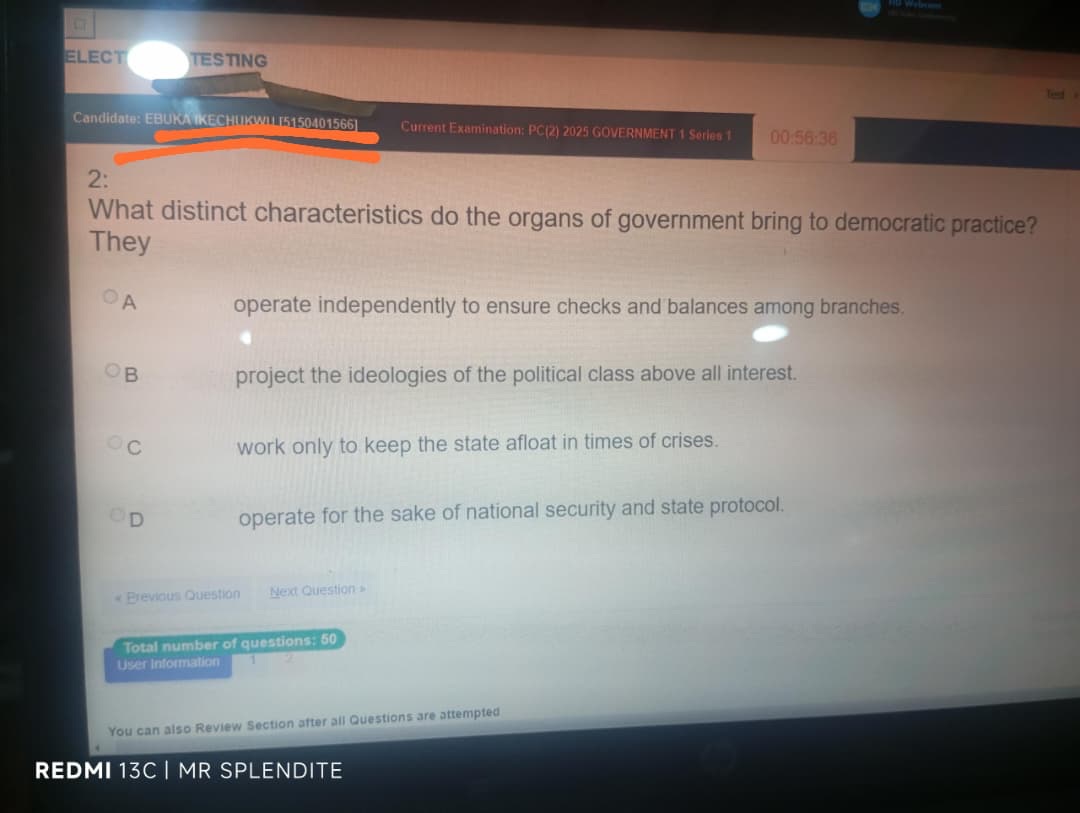
2; (A) operate independently to ensure checks and balances among branches
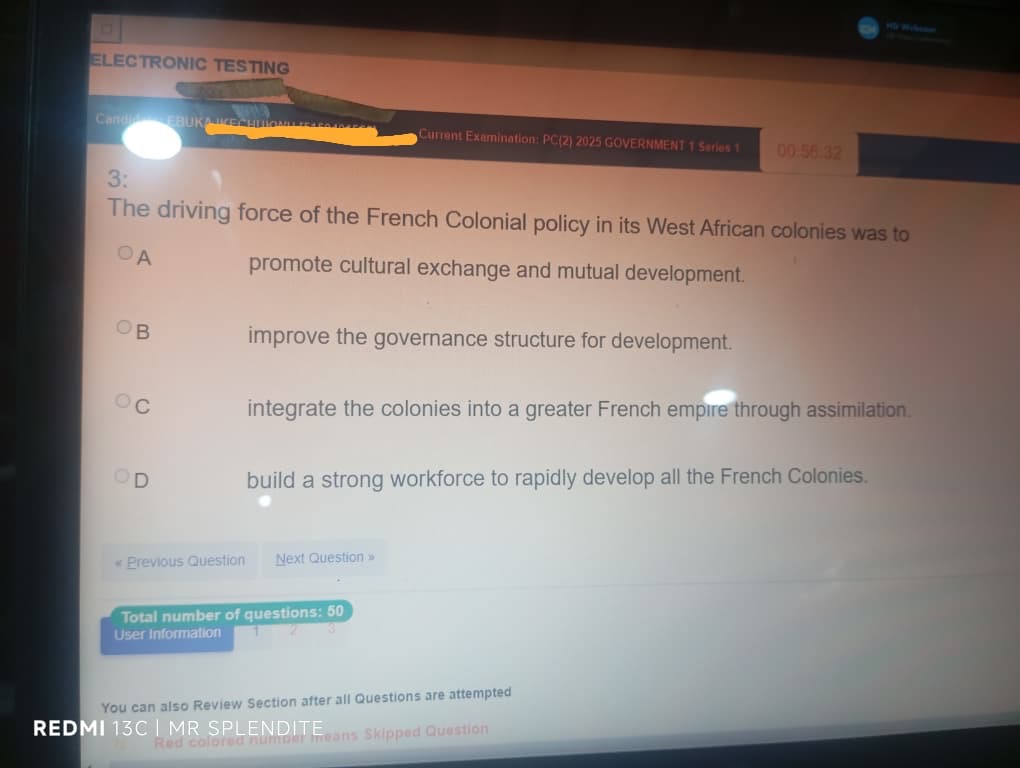
3; (C) integrate the colonies into a greater French empire through assimilation.
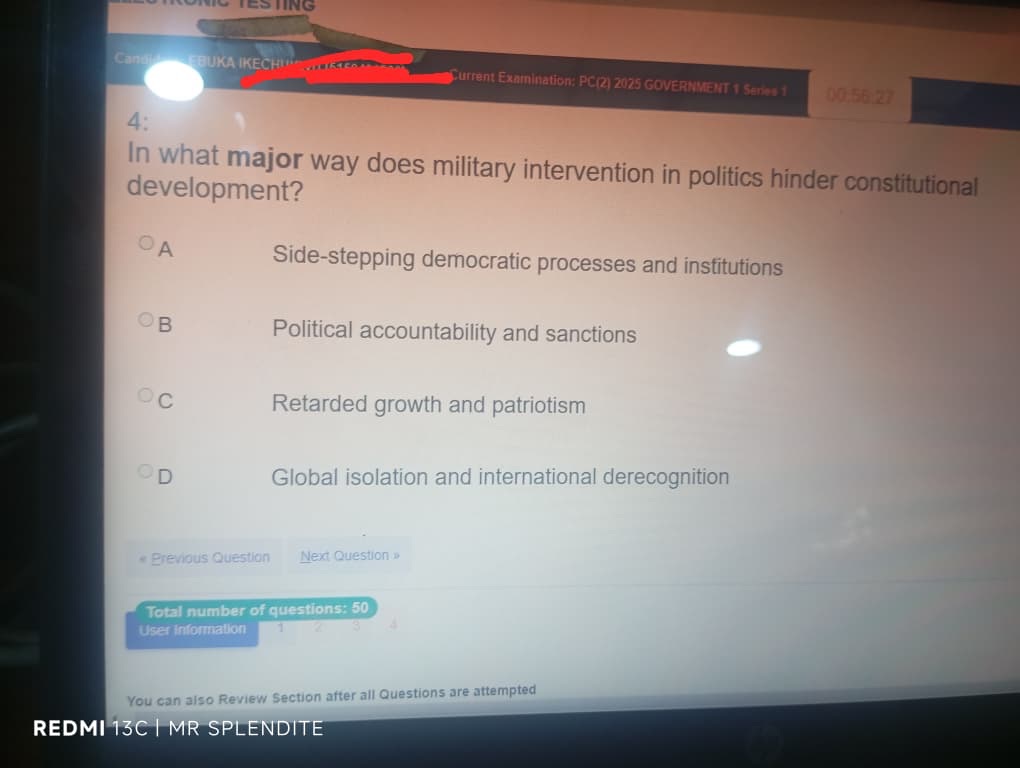
4; (A) Side-stepping democratic processes and institutions
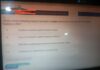
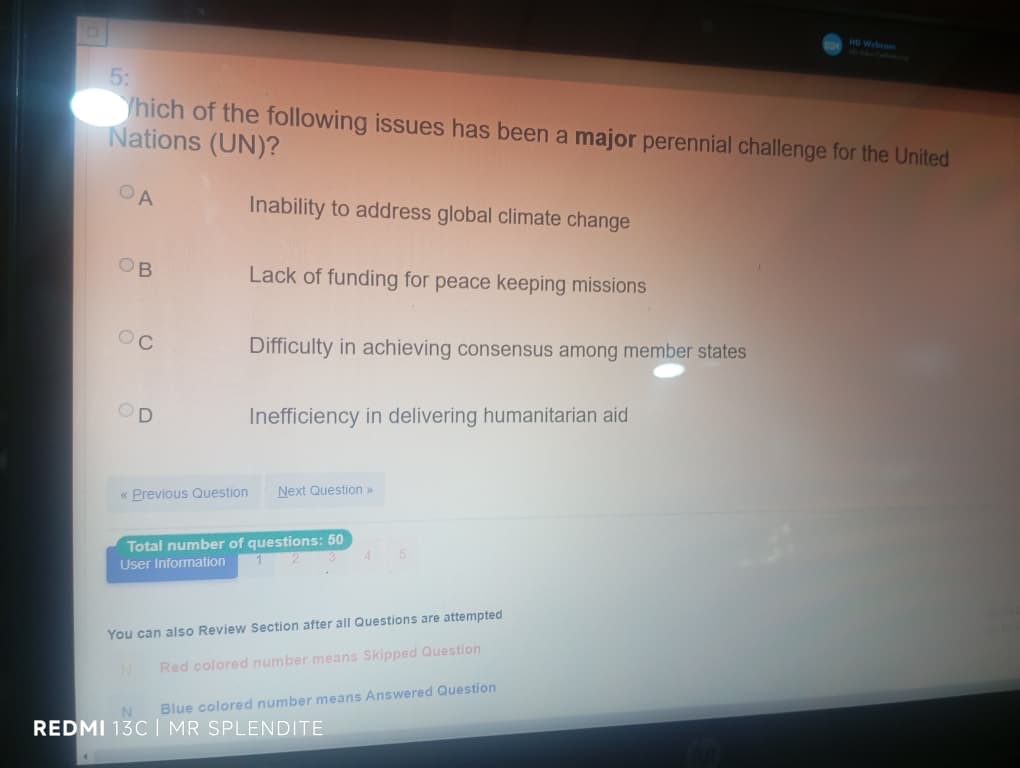
5; (C) Difficulty in achieving consensus among member states
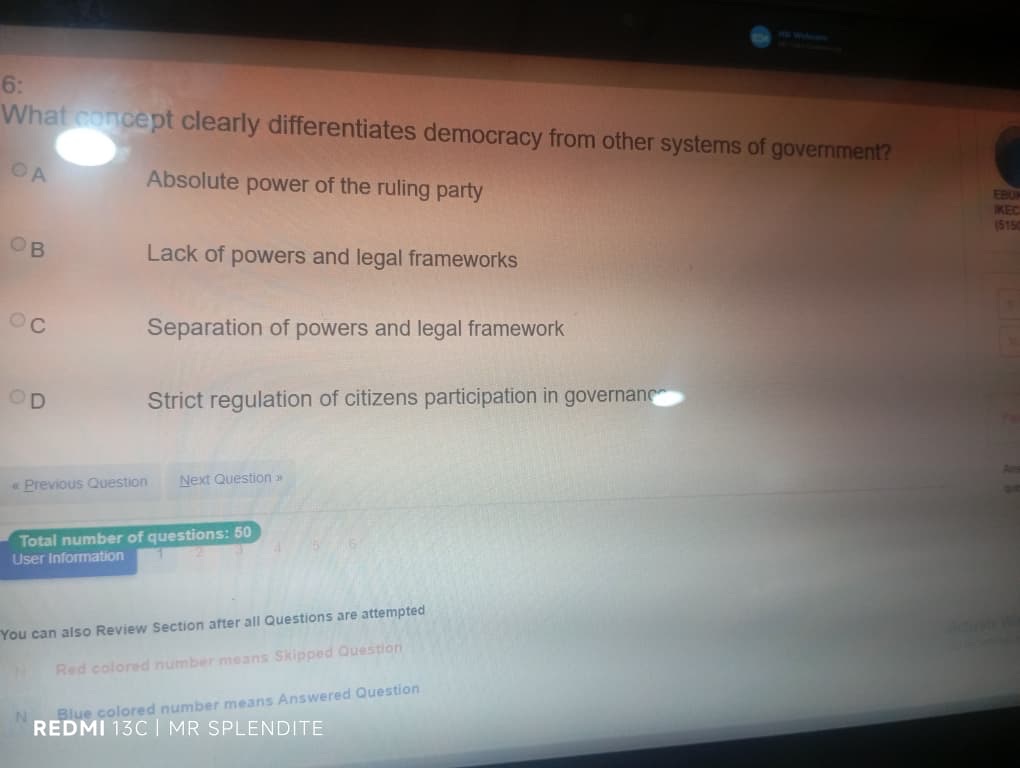
6; (C) Separation of powers and legal framework
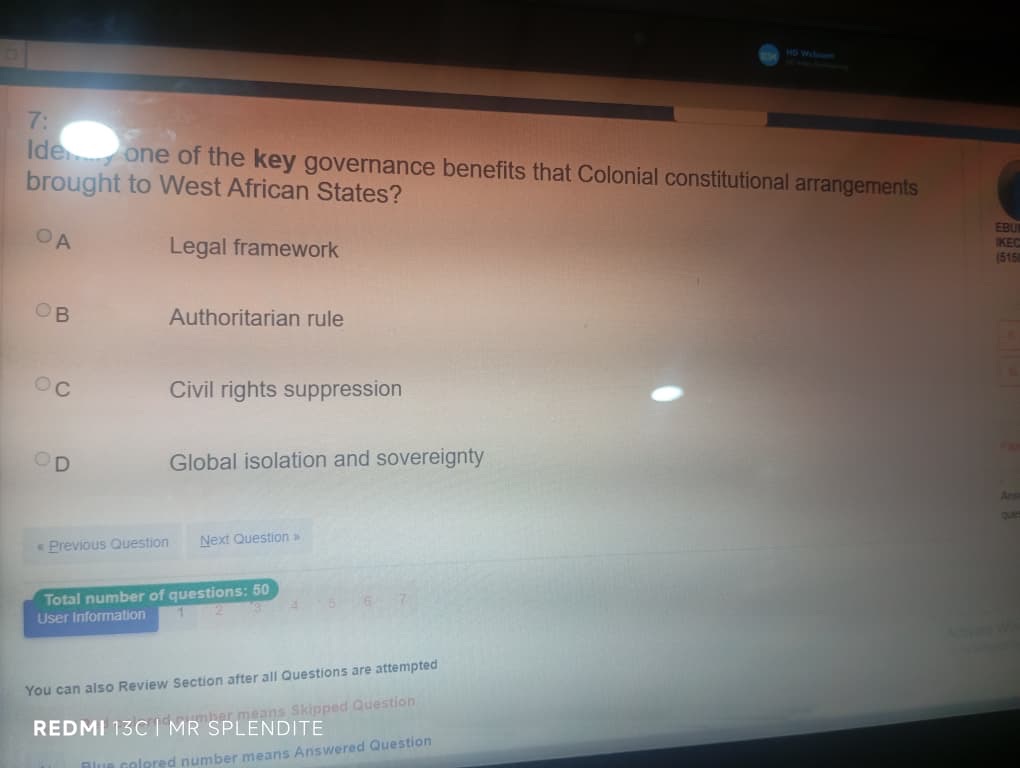
7; (A) Legal framework
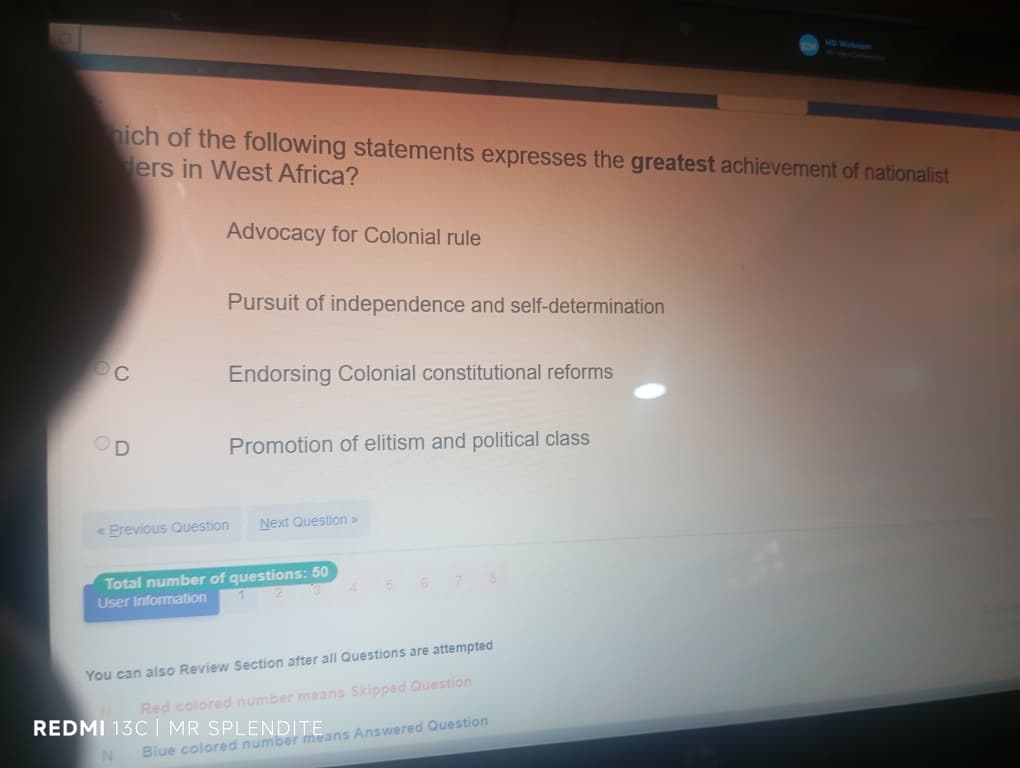
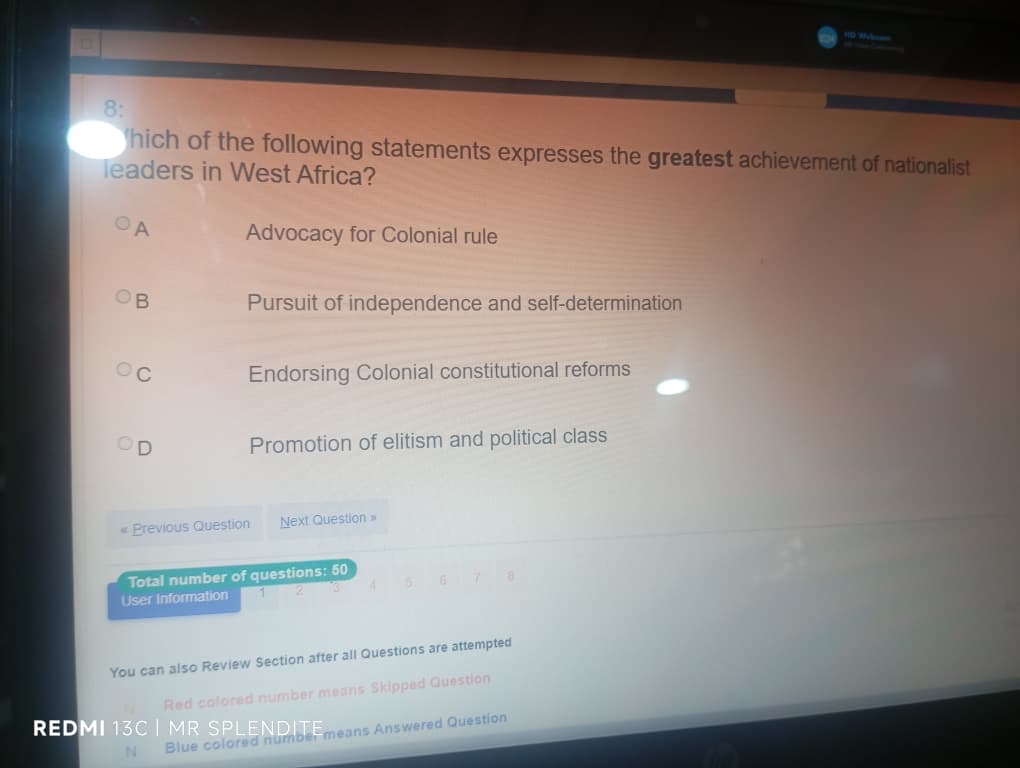
8; (B) Pursuit of independence and self-determination
9;
10;
More coming
*WAEC GCE GOVERNMENT*
*NUMBER NINE*
(9)
(PICK FIVE ONLY)
(i) Limited Participation in Governance: The British restricted Nigerians from holding key administrative positions, which denied them the experience and confidence needed for effective self-government after independence.
(ii) Regional Division and Rivalry: The introduction of regionalism through colonial policies encouraged ethnic and regional divisions that later weakened national unity and political stability.
(iii) Lack of Democratic Training: The colonial administration was largely authoritarian, offering little or no opportunity for Nigerians to learn the principles of democracy, accountability, and good governance.
(iv) Economic Exploitation Over Development: British policies prioritized the extraction of resources for Britain’s benefit, neglecting social and political structures that could have supported Nigeria’s long-term development.
(v) Suppression of Nationalist Movements: The British often arrested or harassed nationalist leaders and restricted political activities, slowing down the growth of political awareness and organization.
(vi) Indirect Rule System: The system strengthened traditional rulers loyal to the colonial masters instead of promoting modern democratic institutions, thereby delaying political modernization.
(vii) Unequal Development Among Regions: British administrative and educational policies favored the South over the North, creating imbalances that later caused political tension and mistrust.
WAEC GCE GOVERNMENT
NUMBER TEN
PICK FIVE
(i) Economic Interdependence: Globalization links Nigeria’s economy with others, making trade, investment, and financial cooperation key factors in foreign policy decisions.
(ii) Foreign Investment and Aid: The need to attract foreign direct investment (FDI) and secure international aid influences Nigeria to maintain friendly relations with developed nations and global institutions.
(iii) Technology and Information Flow: Rapid communication and access to global information shape Nigeria’s diplomatic strategies and response to international issues.
(iv) International Organizations: Membership in global bodies like the UN, WTO, and IMF affects Nigeria’s policy choices and aligns them with global standards.
(v) Security and Terrorism: Global security challenges such as terrorism, piracy, and cybercrime push Nigeria to cooperate with other countries on defense and intelligence matters.
(vi) Cultural Exchange and Migration: The movement of people, ideas, and culture across borders influences Nigeria’s policies on immigration, education, and cultural diplomacy.
(vii) Environmental Concerns: Global issues like climate change and environmental sustainability compel Nigeria to adopt foreign policies that align with international environmental agreements.
(viii) Human Rights and Democracy: Pressure from the international community and global human rights organizations influences Nigeria to promote democratic values and good governance in its foreign policy.
*WAEC GCE GOVERNMENT*
*NUMBER SIX*
(6)
(i) Local Knowledge: Traditional authorities possess in-depth knowledge of local customs, traditions, and social dynamics, providing valuable insights for policymakers and development practitioners, ensuring that interventions are culturally appropriate and contextually relevant.
(ii) Conflict Resolution: Traditional authorities play a crucial role in resolving local disputes and conflicts, mediating between parties, promoting reconciliation, and maintaining social harmony, thereby reducing tensions and fostering peaceful coexistence.
(iii) Community Mobilization: Traditional authorities command respect and influence within their communities, enabling them to mobilize citizens for development initiatives, promote participation in public programs, and foster a sense of collective responsibility.
(iv) Cultural Preservation: Traditional authorities are custodians of cultural heritage, preserving traditions, customs, and values that contribute to social cohesion and identity, promoting cultural tourism, and safeguarding indigenous knowledge.
(v) Governance Legitimacy: Engaging traditional authorities in governance processes enhances the legitimacy and credibility of government institutions, fostering trust and cooperation between the state and local communities, and ensuring that policies are effectively implemented and sustained.
*WAEC GCE GOVERNMENT*
*NUMBER FIVE*
(5)
(PICK FIVE ONLY)
(i) Formulation of Development Oriented Policies: Political parties can serve as platforms for developing sound economic, educational, and social policies that focus on national growth. When parties compete based on well-planned manifestos, it encourages innovation and progressive governance.
(ii) Recruitment and Training of Political Leaders: The party system helps identify, train, and prepare competent individuals for leadership roles. This ensures that qualified and visionary leaders emerge to implement developmental programs effectively.
(iii) Mobilization of Citizens for Participation: Political parties mobilize citizens to participate in elections, policy discussions, and civic activities. Active citizen involvement strengthens democracy and enhances collective efforts toward national development.
(iv) Promotion of Political Stability: When political parties operate peacefully and respect democratic principles, they help maintain political order and reduce conflict. Stability creates a favorable environment for investment and sustainable development.
(v) Policy Continuity and Implementation: A well-structured party system ensures that successive governments within the same party maintain and complete ongoing projects, preventing policy abandonment and wastage of resources.
(vi) Strengthening Accountability and Transparency: Through opposition parties and internal party democracy, the party system promotes checks and balances. Opposition parties hold ruling parties accountable, exposing corruption and demanding better governance.
(vii) Encouragement of National Integration: Political parties that operate across ethnic and regional lines promote unity by bringing together people from diverse backgrounds to work toward common developmental goals.
(viii) Facilitation of Political Education: Parties educate citizens on their rights, duties, and the importance of governance. This political awareness empowers citizens to make informed decisions, support good policies, and demand responsible leadership that fosters development.
Q1
-Protection of fundamental rights – The constitution guarantees citizens’ basic rights such as freedom of speech, religion, and movement.
-Checks and balances – It prevents abuse of power by ensuring each arm of government limits the other.
-Political stability – It provides clear rules for governance, helping to prevent political crises and chaos.
-Rule of law – Everyone is subject to the same laws, promoting fairness and justice.
-Democratic participation : It allows citizens to vote and take part in decision-making processes.
Q2
-Decentralization of power: Powers are shared among federal, state, and local governments for effective administration.
-Unity in diversity : It encourages peaceful coexistence among Nigeria’s various ethnic and religious groups.
-Improved resource management : Each state can develop and control its own natural and human resources.
-Increased political participation :People at different levels of government can participate in politics.
-Balanced development : Developmental projects are spread across all states instead of being concentrated in one area.
Q3
-Policy implementation : Civil servants carry out government policies and programs effectively.
-Advisory role :They advise ministers and government leaders on administrative and technical matters.
-Record keeping and administration : They maintain accurate government records and handle paperwork.
-Service delivery : They provide important services such as education, healthcare, and security to the public.
-Continuity of governance : They ensure smooth running of government even when political leaders change.
Q4
-Checks and balances : The second chamber reviews laws made by the lower chamber to prevent misuse of power.
-Equal state representation : Every state, big or small, has equal representation in national decision-making.
-Improved legislation : Laws go through more debate and correction before approval.
-Prevention of hasty decisions : It allows proper consideration of bills before they become laws.
Strengthening of -democracy : It encourages broader participation and accountability in governance.
Q5
-Policy formulation and implementation :Political parties design and promote development-oriented policies.
-Political education : Parties teach citizens about their rights and responsibilities in government.
-Mobilization of citizens: They encourage people to vote and participate in governance.
-Recruitment of capable leaders : Parties identify and sponsor competent individuals for leadership positions.
-Promotion of accountability: Opposition parties help check government excesses and encourage transparency.
Q6
-Community mobilization : Traditional rulers can organize their people for community and government projects.
-Conflict resolution : They help settle local disputes peacefully to maintain order and stability.
-Policy acceptance :Their support for government policies increases citizens’ willingness to comply.
-Preservation of culture and values: They uphold moral values, discipline, and cultural heritage within communities.
-Information dissemination :They help spread government information quickly to rural and local communities.
*WAEC GCE GOVERNMENT*
*NUMBER FOUR*
(4)
(PICK FIVE ONLY)
(i) Promotion of Checks and Balances: The second chamber helps to check the excesses of the lower chamber (House of Representatives) and the executive arm. This ensures that no single organ of government becomes too powerful, thereby strengthening democracy and accountability.
(ii) Representation of States Equally: In Nigeria’s federal structure, the Senate ensures equal representation of all states, regardless of population size. Each state has the same number of senators, promoting fairness and protecting the interests of smaller states.
(iii) Quality Legislation: Having a second chamber allows bills and policies passed by the lower chamber to undergo further scrutiny, debate, and amendment. This double-checking process improves the quality and effectiveness of laws enacted.
(iv) Prevention of Hasty Legislation: The Senate serves as a reviewing body that carefully examines proposed laws, preventing rash or poorly thought-out legislation that might harm national interests.
(v) Promotion of Political Stability: By allowing wider consultation and deliberation before passing laws, the second chamber reduces political tension and promotes consensus-building among different political groups and regions.
(vi) Protection of Minority Interests: The Senate provides a platform where minority groups and less populous regions can express their views and defend their interests, thereby promoting inclusiveness and national unity.
(vii) Support for National Integration: Through equal state representation, the second chamber encourages cooperation among diverse ethnic and regional groups, fostering unity and a stronger sense of belonging within the federation.
(viii) Oversight and Accountability Functions: The Senate plays a vital role in overseeing the activities of the executive arm, approving key appointments, and investigating government actions, thereby enhancing transparency and good governance.
*WAEC GCE GOVERNMENT*
*NUMBER THREE*
(3)
(PICK FIVE ONLY)
(i) Policy Implementation: Civil servants are responsible for carrying out government policies and ensuring that the decisions made by the executive and legislature are effectively implemented.
(ii) Policy Advice: They provide expert and professional advice to ministers and political leaders on matters of governance, administration, and development planning.
(iii) Administrative Continuity: Civil servants ensure stability and continuity in government operations, even when there is a change in political leadership or administration.
(iv) Record Keeping and Documentation: They maintain accurate and up-to-date records of government activities, policies, and expenditures, which are essential for accountability and future reference.
(v) Public Service Delivery: Civil servants manage and deliver essential public services such as education, healthcare, transportation, and security to citizens.
(vi) Regulation and Supervision: They enforce government laws, rules, and regulations to ensure order, discipline, and compliance within society and the public sector.
(vii) Budget Preparation and Financial Management: Civil servants prepare government budgets, manage public funds, and ensure the efficient use of financial resources for national development.
(viii) Representation and Liaison: They act as a link between the government and the public, as well as with international organizations, ensuring smooth communication and cooperation.
*WAEC GCE GOVERNMENT*
*NUMBER TWO*
(2)
(PICK FIVE ONLY)
(i) Promotion of Unity in Diversity: The federal system allows various ethnic, religious, and cultural groups in Nigeria to coexist peacefully under one nation while maintaining their unique identities, thereby fostering national unity.
(ii) Decentralization of Power: By dividing powers between the federal, state, and local governments, federalism ensures that governance is closer to the people. This makes administration more effective and responsive to local needs.
(iii) Encouragement of Grassroots Development: Federalism enables state and local governments to initiate and execute developmental projects that address specific community challenges, promoting balanced regional development.
(iv) Political Participation: The system provides multiple levels of government where citizens can participate in politics, contest elections, or engage in decision-making processes, thereby deepening democracy.
(v) Resource Management and Allocation: Federalism allows regions to have a degree of control over their resources and encourages competition in development efforts, promoting economic growth and efficient resource utilization.
(vi) Conflict Management: By giving autonomy to different regions, the federal structure helps reduce political and ethnic tensions that could arise from over-centralization, thereby promoting peace and stability.
(vii) Strengthening of Institutions: Federalism promotes the establishment of multiple government institutions at various levels, which enhances administrative efficiency, accountability, and institutional growth.
(viii) Promotion of Innovation and Healthy Competition: States are encouraged to develop innovative policies and compete in areas such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure, contributing to overall national progress.
*WAEC GCE GOVERNMENT 2025*
*NUMBER 6*
(6)
(i) *Maintenance of Law and Order:* Traditional rulers serve as valuable intelligence gatherers for formal security agencies and use customary methods to mediate disputes (e.g., land, family, minor civil cases) before they escalate into major conflicts.
(ii) *Facilitation of Community Mobilization for Development Projects:* Traditional leaders command significant respect and authority, making them effective in mobilizing their subjects for community self-help projects, such as building schools, health centers, and feeder roads.
(iii) *Enhancing Communication between Government and the People:* Traditional rulers help interpret and disseminate government policies and programs to the local populace in a culturally sensitive manner, while also providing feedback to the government on the needs, concerns, and interests of their communities.
(iv) *Preservation and Promotion of Cultural Heritage and National Identity:* As custodians of indigenous culture, customs, and traditions, traditional institutions help maintain social cohesion and a sense of national identity amidst Nigeria’s diverse ethnic landscape. By promoting cultural festivals and traditional values, they can also attract tourism and foster unity, contributing to nation-building.
(v) *Strengthening Local Governance and Accountability:* Traditional leaders can offer non-partisan advice to local and state governments on matters of customary law, land administration, and community affairs.
*WAEC GCE GOVERNMENT*
*NUMBER ONE*
(1)
(PICK FIVE ONLY)
(i) Protection of Fundamental Rights: Constitutional governance guarantees the protection of citizens’ fundamental human rights such as freedom of speech, religion, and association. This assurance of liberty encourages people to support and uphold the system.
(ii) Rule of Law: It ensures that all individuals and institutions, including government officials, are subject to the law. This promotes fairness, justice, and equality before the law, which builds citizens’ confidence in governance.
(iii) Accountability of Leaders: Constitutional governance provides mechanisms through which public officials are held accountable for their actions. This reduces corruption and abuse of power, thereby earning the trust and support of the people.
(iv) Political Stability: By clearly defining the roles and powers of each arm of government, constitutional governance minimizes political conflicts and promotes stability, which encourages citizens to embrace the system.
(v) Democratic Participation: It promotes citizens’ involvement in political processes through free and fair elections, referendums, and public consultations. This sense of inclusion motivates people to support constitutional governance.
(vi) Protection of Minority Rights: The constitution safeguards the interests and rights of minority groups, preventing domination by the majority. This inclusivity fosters unity and acceptance of the political system.
(vii) Separation of Powers: Constitutional governance ensures that powers are divided among the executive, legislative, and judicial arms of government. This prevents tyranny and promotes checks and balances, encouraging citizens’ confidence.
(viii) Promotion of National Development: A constitutionally guided government provides a stable political environment that attracts investment, promotes justice, and supports economic and social development, motivating people to uphold it.
Noted all this information was posted after its surface online and I decided to post to get Adsense approval